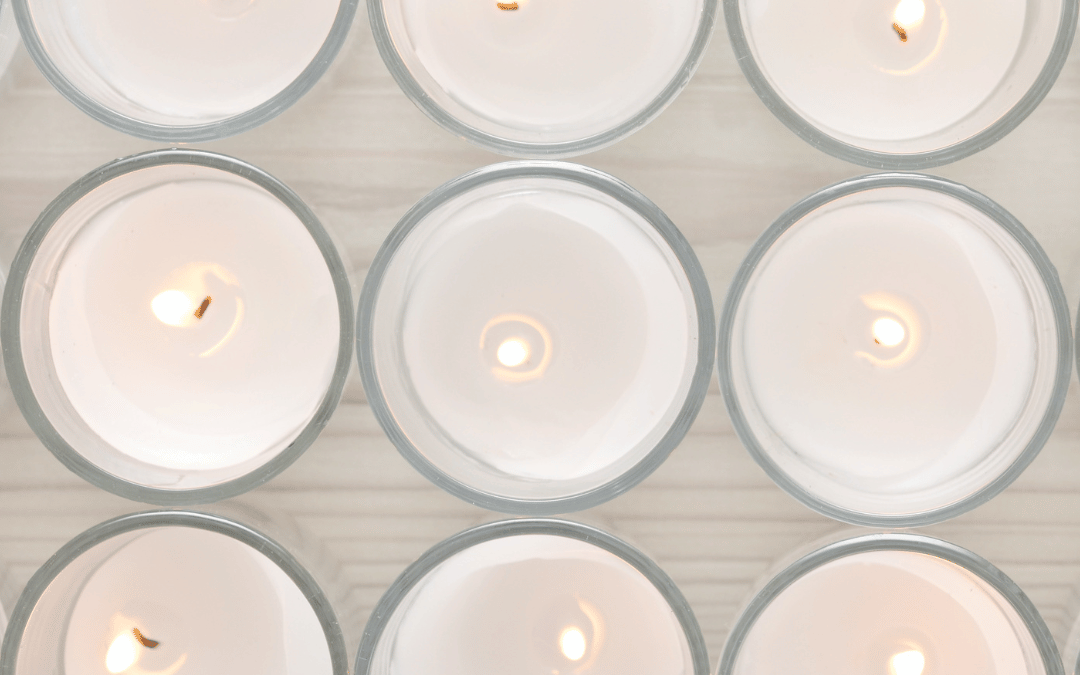
Have you ever wondered where the wax goes as your candle burns down to nothing? At Candle Creations, we love unraveling the mystery behind that magical disappearing act. What seems like a vanishing trick is actually a fascinating journey of candle science, and we’re here to break it down for you!
What Is Candle Wax Made Of?
Candle wax, whether it’s our favourite soy, classic paraffin, or natural beeswax, is crafted from long-chain hydrocarbons. These are made of hydrogen and carbon atoms, which keep the wax solid at room temperature. This sturdy form lets us pour wax or mold wax into delightful shapes, ready to burn slowly and steadily.
The Burning Process Unveiled
Every candle is a duet of wax and wick, working in harmony. The wax is your candle’s main fuel, but it can’t burn solo. It needs the wick’s fiery touch to start the process of combustion—our candle’s way of shining bright.
When you light the wick, the flame’s heat melts the surrounding wax, turning it into a silky liquid. Imagine the wick as a tiny straw, sipping up the liquid wax through capillary action, and delivering it straight to the flame.

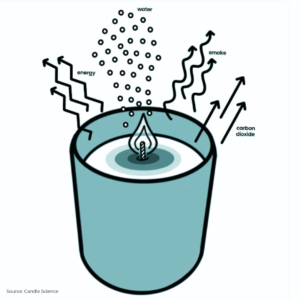
Here’s where the real magic happens: the heat from the flame turns the liquid wax into flammable gas vapour. When this vapour mingles with oxygen, it bursts into a lively dance of light and warmth, producing:
- A cozy glow and gentle heat
- A sprinkle of soot and smoke
- Carbon dioxide
- Water vapour
This performance continues as long as there’s wax and air to fuel it. But remember, for safety and the best experience, it’s wise to let your candle burn for only 3-4 hours at a time.
The Magical Transformation
So, where does the wax go? The candle’s wax transforms through combustion, a fiery reaction with oxygen and heat. This process turns your solid wax into invisible carbon dioxide and water vapour, leaving but a memory—and a lovely fragrance—in the air.
So now you know where the wax goes – fascinating eh?






